Xceed Workbooks for .NET v3.0 Documentation

'DeclarationPublic Class LineSeries Inherits Series
'UsageDim instance As LineSeries
public class LineSeries : Series
The code below would display the following Chart:
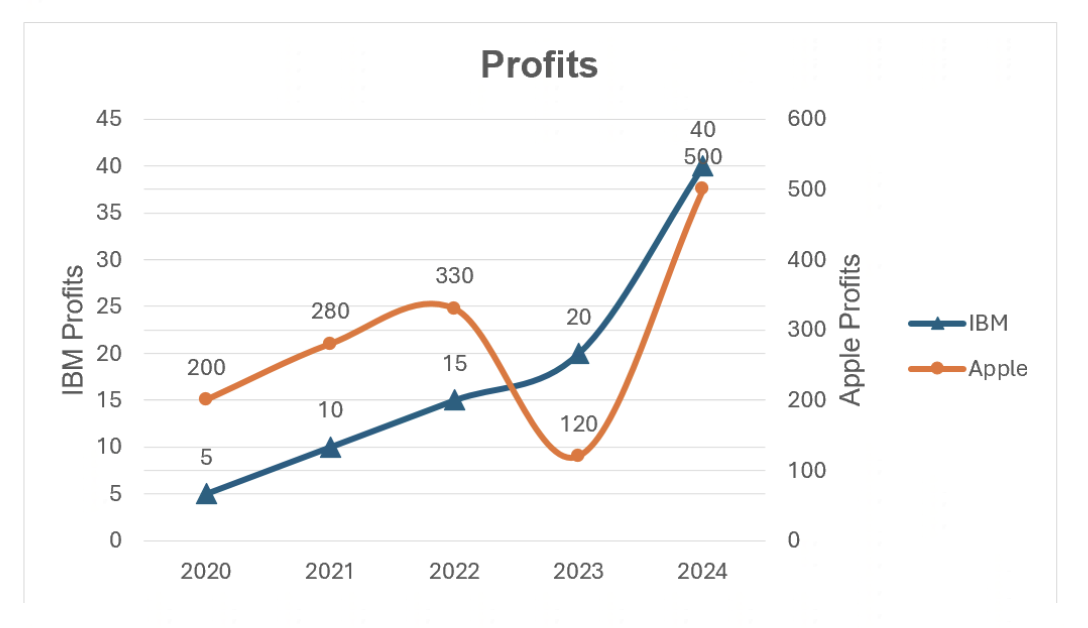
var workbook = Workbook.Create( ChartSample.ChartSampleOutputDirectory + @"AddCharts.xlsx" ); // Gets the first Worksheet. A Workbook always contains at least 1 Worksheet. var worksheet = workbook.Worksheets[ 0 ]; // Adds Values for Category. worksheet.Cells[ "B4" ].Value = 2020; worksheet.Cells[ "B5" ].Value = 2021; worksheet.Cells[ "B6" ].Value = 2022; worksheet.Cells[ "B7" ].Value = 2023; worksheet.Cells[ "B8" ].Value = 2024; // Adds Values for Series. worksheet.Cells[ "C4" ].Value = 200; worksheet.Cells[ "C5" ].Value = 280; worksheet.Cells[ "C6" ].Value = 330; worksheet.Cells[ "C7" ].Value = 120; worksheet.Cells[ "C8" ].Value = 500; // Adds a LineChart with the generic Add method and set its SubType. The size of the Chart will be from Cell E4 to L18. var lineChart = worksheet.Charts.Add<LineChart>( "E4", "L18" ); lineChart.SubType = LineChartSubType.LineWithMarkers; // Sets the Chart's Title. lineChart.Title.Text = "Profits"; lineChart.Title.TextOptions.Font.Bold = true; // Sets the Legend. lineChart.Legend.Position = LegendPositionType.Right; // Sets the Category data(x values) for the LineChart : Cells B4 to B8. lineChart.CategoryData = CategoryData.FromCells( worksheet, "B4", "B8" ); // Adds LineSeries to the LineChart (y values) by specifying fixed values and a range of Cells’ Adresses. var lineSeries1 = lineChart.SeriesCollection.AddFromValues<LineSeries>( 5, 10, 15, 20, 40 ); lineSeries1.Name = "IBM"; var lineSeries2 = lineChart.SeriesCollection.AddFromCells<LineSeries>( "C4", "C8" ); lineSeries2.Name = "Apple"; // Customizes the LineSeries’ Markers. lineSeries1.Marker.Symbol = MarkerSymbol.Triangle; lineSeries1.Marker.Size = 8; lineSeries2.Marker.Symbol = MarkerSymbol.Diamond; lineSeries2.Marker.Size = 8; // Smoothes the LineSeries. lineSeries1.IsSmoothed = true; lineSeries2.IsSmoothed = true; // Shows the LineSeries’ DataPoint labels value and position them. lineSeries1.DataPointLabels.ShowValue = true; lineSeries1.DataPointLabels.Position = PointDataPointLabelsPositionType.Above; lineSeries2.DataPointLabels.ShowValue = true; lineSeries2.DataPointLabels.Position = PointDataPointLabelsPositionType.Above; // Draws the LineSeries2 on the 2nd ValueAxis. lineSeries2.PlotOnSecondaryAxis = true; // Sets titles for the 2 ValueAxis. lineChart.ValueAxis.Title.IsVisible = true; lineChart.ValueAxis.Title.Text = "IBM Profits"; lineChart.SecondaryValueAxis.Title.IsVisible = true; lineChart.SecondaryValueAxis.Title.Text = "Apple Profits"; // Saves Workbook to disk. workbook.Save();
System.Object
Xceed.Workbooks.NET.WorkbookElement
Xceed.Workbooks.NET.WorksheetElement
Xceed.Workbooks.NET.ChartValueRange
Xceed.Workbooks.NET.Series
Xceed.Workbooks.NET.LineSeries
| Name | Description | |
|---|---|---|
 | LineSeries Constructor | Creates a LineSeries in the Chart. |
| Name | Description | |
|---|---|---|
 | CellRange | Gets the CellRange associated with the ChartValueRange. (Inherited from Xceed.Workbooks.NET.ChartValueRange) |
 | DataPointLabels | Gets the LineSeries' data labels. |
 | Fill | Gets the Area that will be filled with a color. (Inherited from Xceed.Workbooks.NET.Series) |
 | IsSmoothed | Gets or sets if the LineSeries will smooth the lines drawn around data points. |
 | Marker | Gets the LineSeries' Markers. |
 | Name | Gets or sets the Series' name. (Inherited from Xceed.Workbooks.NET.Series) |
 | PlotOnSecondaryAxis | Gets or sets if the Series is plotted on the secondary Axis. (Inherited from Xceed.Workbooks.NET.Series) |
 | Stroke | Gets the Line associated with the Series. (Inherited from Xceed.Workbooks.NET.Series) |
 | SubType | Gets or sets the LineChartSubType. |
 | Values | Gets or sets the values associated with the ChartValueRange. (Inherited from Xceed.Workbooks.NET.ChartValueRange) |
.NET: net5.0, net5.0-windows, net6.0, net6.0-macos, net6.0-windows, net7.0, net7.0-macos, net7.0-windows, net8.0, net8.0-browser, net8.0-macos, net8.0-windows, net9.0, net9.0-browser, net9.0-macos, net9.0-windows, net10.0, net10.0-browser, net10.0-macos, net10.0-windows.
.NET Framework: net40, net403, net45, net451, net452, net46, net461, net462, net463, net47, net471, net472, net48, net481.